

There are also applications based on other side-effects of slowing light down.

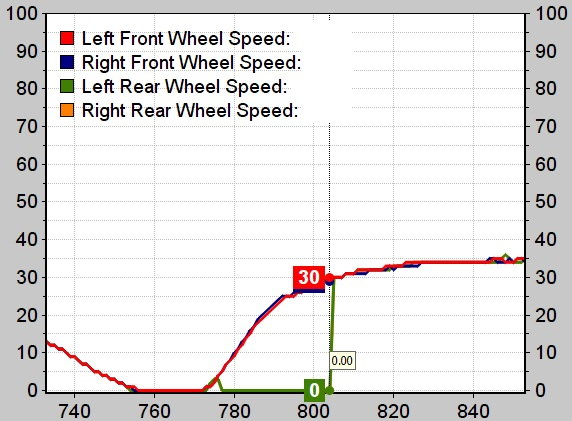
A ten-centimetre cell filled with hot rubidium gas should be able to do the same thing more efficiently. At present, they do this by sending one of the pulses along lots of optical fibre built especially for this purpose. Sometimes, engineers sending pulses of light through cables need to delay one signal compared with another. Atac Imamoglu, an optical engineer at the University of California, Santa Barbara, thinks that other applications in communications will arise from the simple fact that light can be made to take much longer than usual to travel from place to place. It is just this type of property that makes engineers who design optical switches rub their hands with glee.Īnd that's not all. In the case of heated rubidium, a slight alteration in the frequency or strength of one of the laser beams entering the cloud can abruptly absorb the light and stop it from being transmitted. Non-linearity, however, means that a tiny change in the property of the light going in causes a huge change in the property of the light coming out. In most cases, light behaves in a straightforward fashion: double the intensity of the light going into a piece of glass, for instance, and you double the intensity of the light coming out of it. One is to produce what is called an extremely high non-linearity in the material that does the slowing. Slowing light down this way also has other effects. And second, the interference between the two beams creates a third, very long wavelength beam which propagates much more slowly than either of the wavelengths of which it is composed. First, it puts the atoms into a delicate quantum state that does not allow them to absorb light. Dr Welch does this by making two pulses of light with slightly different wavelengths interact. So the trick is to get the light to slow down without being absorbed this way. In such cases, the interaction is weak, and any attempt to strengthen it tends to result in the light being absorbed. Light slows down a little even when it passes through ordinary transparent materials, such as glass or water, because it interacts with the atoms that the material is made of. It involved heating up a special transparent container known as a cell, that contained solid rubidium metal, to about the boiling point of water, and then sending in two finely tuned beams of light produced from the same sort of laser that is used in a compact-disc player. And to do an experiment with hot rubidium was much simpler. If applications based on slow light are to become a realistic possibility, there needs to be a cheaper, easier way to do the trick.ĭr Welch, a physicist at Texas A&M University, realised that the same fundamental physics that worked to slow light down in cold sodium atoms would also work in hot rubidium. But chilling atoms down to just a few billionths of a degree above absolute zero is a difficult task which requires equipment costing hundreds of thousands of dollars. With such a huge change in this fundamental property of nature, all sorts of things might become possible, including novel ways to store and transmit information, and new devices based on light, such as optical switches.Ī few months ago, a group of researchers from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and Stanford, California, thrilled the world with demonstrations of light travelling at a lazy 17 metres per second as it passed through a collection of cold sodium atoms.
#SPEED OF LIGHT MPH HOW TO#
In a recent issue of Physical Review Letters, Dr Welch and his colleagues describe how to slow light down from 300m metres per second to a mere 90 metres per second by sending it through a hot gas made of rubidium atoms. But take a beam of light after George Welch is done with it, and even a small aeroplane would be able to beat it.
#SPEED OF LIGHT MPH FULL#
Symbols, abbreviations, or full names for units of length,Īrea, mass, pressure, and other types.IN NORMALcircumstances, nothing can travel faster than light. You can find metric conversion tables for SI units, as wellĪs English units, currency, and other data. It is commonly abbreviated in everyday use in the United States, the United Kingdom, and elsewhere to mph or MPH, although mi/h is sometimes used in technical publications.Ĭonversion calculator for all types of measurement units. Miles per hour is a unit of speed, expressing the number of international miles covered per hour. Mph to speed of light, or enter any two units below: Enter two units to convert From: You can do the reverse unit conversion from


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
